6 commonly googled health insurance questions

With a range of health insurance policies to choose from, deciding what cover would best suit you or your family can feel like a daunting task. This is why we have found commonly asked questions about health insurance and answered them for you – Real simple.
Read on to learn the answers to 6 commonly googled questions on health insurance in Australia.
1. How does private health insurance work in Australia?
While Australians have access to Medicare, (the public healthcare system) there are still healthcare costs that may not covered by Medicare – like physiotherapy and dental.
There are 3 main reasons to choose private hospital cover in addition to the public healthcare system:
- Private hospital room – while this isn’t a guarantee, having private health insurance can increase your chance of having your own room during your hospital stay.
- Choice of doctor – you have the ability to choose a doctor that you are comfortable with. Typically, in the public system, a doctor is assigned to you.
- Skip the queue – the wait time in the public system can be weeks, even months. Here are the median hospital wait times for common procedures:
- Knee Replacement – 308 days¹
- Hip Replacement – 179 days¹
- Tonsils Removal – 174 days¹
- Coronary Bypass – 19 days¹
Another reason people may want to take out private health cover is that having even the most basic hospital cover may allow you to pay less tax by avoiding the Medicare levy surcharge. You may also be eligible for the private health insurance rebate, if you earn less than the income threshold and have a high enough level of hospital cover. This can either reduce your insurance premium or be a tax offset on your income tax return.
Plus, taking out private health cover can mean you're able to save money and claim deductions of some medical treatments or services, such as dental care and optical visits. Make sure to check what annual limits apply to your health fund and any waiting periods that may apply to your policy.
2. What happens if you don't have private health insurance after 30?
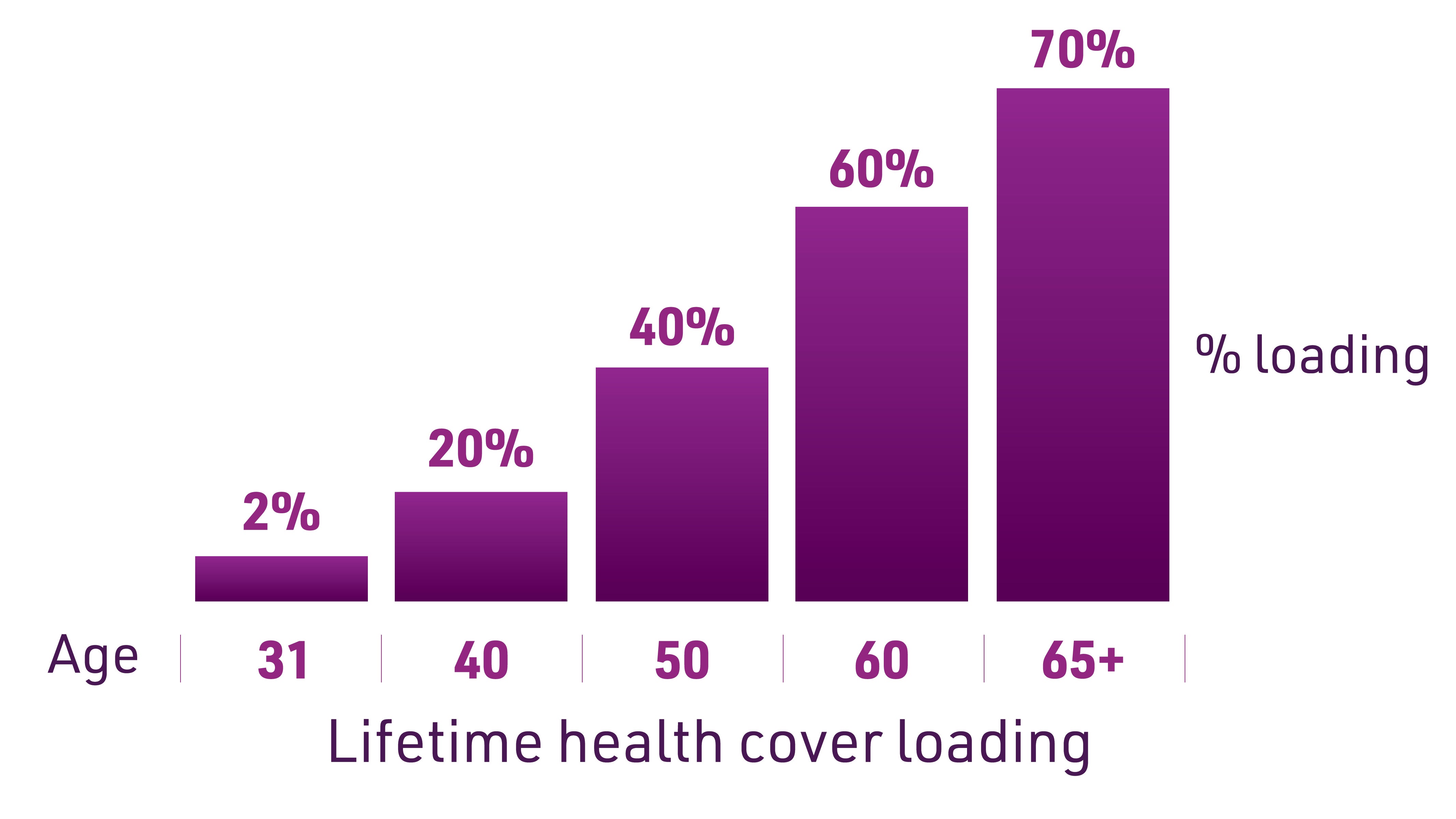
The Australian Government encourages people to take out private hospital cover before 1 July following their 31st birthday under the initiative known as Lifetime Health Cover (LHC).
Under LHC, if you don’t have hospital cover following your 31st birthday, you’ll need to pay an extra 2% on insurance premiums each year that you’ve put off private hospital cover after turning 31. You’ll be required to pay the loading for ten consecutive years before it ceases, and the maximum loading is 70%. This can equate to thousands of extra dollars you’ll need to pay when you eventually take out private hospital cover.
3. Is ambulance cover part of health insurance?
Ambulance bills can be in the hundreds to thousands of dollars. Thankfully, the costs can be covered by hospital cover or extras cover with private health insurance.
Emergency ambulance transport to hospital (provided by a state or territory ambulance service) is included – that's air, land, and sea transport Australia wide! If you live in QLD or TAS you are already covered under your states scheme and this cover remains if you are travelling interstate. In NSW and ACT, Pensioner, Concession or Health care card holders receive ambulance services free of charge under the Provision of Ambulance provided by NSW Ambulance.
4. What is the private health insurance rebate?
The private health insurance rebate is a financial incentive provided by the Australian government to help reduce the cost of private health insurance premiums. The rebate can also be claimed as a tax credit when you lodge your tax return with the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) if you do not wish to use it to reduce your premium.
If you currently hold private health insurance, you could be eligible to receive a rebate. The amount received will depend on the following criteria:
Income tiers: The private health insurance rebate is income tested, so if your taxable income is higher than the relevant income threshold, you may not be eligible for a rebate. Your rebate entitlement depends on your family status on 30 June, with different thresholds applying depending on whether you have a single income or a family home.
- Single income thresholds: If you are single on the last day of the income year and have no dependents, your income is tested against the single income thresholds. This applies even if you have a spouse for the majority of the year, as long as you are single, on 30 June of the income year.
- Family income thresholds: If you had a spouse on the last day of the income year, your income would be tested against the family income thresholds, with your entitlement to a rebate being assessed on you and your spouse’s combined income.
Age: Older individuals generally receive a higher rebate than younger individuals. For instance, Australians aged 65-69 will likely receive a higher rebate compared to those under 65.
5. Can you still use Medicare if you have health insurance?
If you have private health insurance, you can still use Medicare services and access the public hospital system. Using Medicare is at no cost to you as the patient, and, in some instances, there are times when you can claim Medicare benefits and use your private health insurance at the same time.
For instance, if you go to a public hospital as a private patient, you may be eligible to claim the costs covered by Medicare and some of the costs through your private insurance. In this instance, you can submit a Medicare claim form and a Medicare two-way claim form.
6. Is private health insurance worth it?
Despite Australia boasting a good public healthcare system, private health insurance may be worth considering covering healthcare costs not covered by Medicare. There is also the Medicare levy surcharge to consider. This is a tax that applies to those earning over $97,000, where 1 to 1.5% of your income will go to the public health system. But may not have to pay this if you have health insurance.
Private health insurance can help pay for a wide range of medical treatments and health care costs that may not be covered by Medicare, such as dental, optical services, and physiotherapy. This is known as Extras cover.
Private health insurance can provide access to your choice of doctors, specialists, and hospitals. Plus, you’ll likely experience shorter waiting times for elective surgeries and specialist appointments as well. This is known as Hospital cover.
Interested in learning more about Real Health Insurance? You can get a quote online now.
13 Sept 2024
References
1. Median elective surgery waiting times sourced from Australian Institute of Health and Welfare data, Public Hospital wait time for public patients (days) 2022 - 2023. Actual wait times vary by hospital and severity of the condition. Category wait times are used where specific procedure wait times are not available.